
The process begins with the issuance of an invoice to the tenant, detailing the amount owed and the due date. This invoice serves as the primary document for recording the receivable in the accounting system. When lease terms are renegotiated, it may necessitate remeasuring the rent receivable and adjusting the related accounts. This could involve recalculating the present value of future lease payments and recognizing any gain or loss resulting from the modification. Advanced accounting software like NetSuite or Sage Intacct can be invaluable in managing these complex entries, providing automated solutions that ensure accuracy and compliance with accounting standards.
Rent Receivable in Lease Accounting
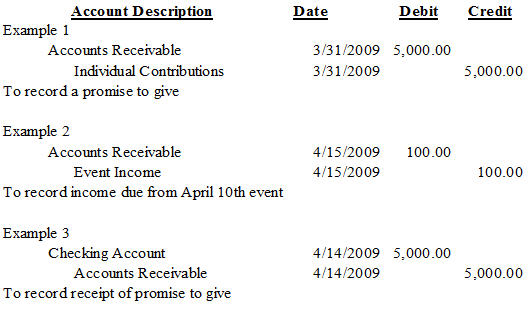
Such a receipt is often treated as an indirect income and recorded in the books with a journal entry for rent received. Rent revenue is usually earned through the passage of time when the company leases or rents out the equipment or property to its lessee. Likewise, the amount of rent revenue will be accrued during the rent period.
Accounting and Journal Entry for Rent Received
Generally, accounting for the same lease under ASC 840 (before transition to ASC 842) and then under ASC 842 (after transition) has no impact on an entity’s net income. How do you calculate the lease liability, ROU asset, and straight-line rent expense for the scenario above? In order to arrive at the correct answer under US GAAP, we need to sum the total net lease payments and then divide those payments by the total number of periods in the lease term. Accrued rent is another liability account under ASC 840 that is derived from a difference in the timing of cash payment and expense recognition.
What are the prerequisites for recording an entry?
This not only enhances security but also simplifies the reconciliation process, reducing the risk of discrepancies and disputes. Smart contracts, a feature of blockchain, can automate rent collection and enforce lease terms, further streamlining operations. The introduction of these standards has also brought about the need for detailed disclosures. Lessors must provide comprehensive information about their lease receivables, including maturity analyses and the nature of the lease payments. This level of detail helps stakeholders understand the financial implications of lease agreements and assess the lessor’s exposure to credit risk.
Most often, deferred rent was a liability that increased over the first part of the lease term as payments start low and gradually increase. Under ASC 842, those balances are no longer on the balance sheet but are reflected as adjustments to the ROU asset balance. In practice, lease payments are not typically disbursed at a constant amount, even if they are recognized in that manner. The recognition of rent receivables must adhere to the accrual basis of accounting, where revenue is recorded when earned, not necessarily when received. This principle ensures that financial statements reflect the true financial position of the business. For instance, if rent is due on the first of the month but not paid until the fifteenth, the receivable is still recorded on the first.
- The introduction of these standards has also brought about the need for detailed disclosures.
- The Rent Receivable account is also important for tax purposes, as it accurately reflects the amount of money that has been earned over a certain period of time.
- The tenant would prepare an amortization table under ASC 842 to assist with the calculation of the periodic entries moving forward.
- The debit for this journal entry will be to rent expense, increasing expense on the income statement.
- Example – On 10th March, XYZ Ltd paid office rent to its landlord by cheque for the same month amounting to 20,000.
- Accrued rent is another liability account under ASC 840 that is derived from a difference in the timing of cash payment and expense recognition.
Let’s see the what’s the journal entry to record after the credit period is complete. Accountants needs to capture every financial transaction precisely in the books of accounts. The stakeholders will be able to get a true picture of business operations.
In this example, it is the liability of $11,254,351 minus the incentive balance of $200,000. The lease term is 120 months (from step 1) and total rent is $15,767,592 (from step 1). Straight-line monthly rent expense calculated from base rent is therefore $131,397 ($15,767,592 divided by 120 months). After the effective date of ASC 842, the differences in the timing of cash flows and expense recognition will continue to be reflected in adjustments to the ROU asset balance. Under both ASC 840 and ASC 842, the formula to calculate straight-line rent expense is total net lease payments divided by the total number of periods in the lease. By utilizing blockchain for rent transactions, property managers can create a transparent and immutable record of all payments.
Under ASC 842, accrued rent is no longer recognized as its own line item on the financial statements. Deferred rent is the result of rent expense being recorded on a straight-line basis when cash paid for rent escalates or de-escalates over the term of the lease. Under ASC 840, the lessee records the straight-line rent expense and captures any difference between the cash paid and the expense recognized by debiting and crediting deferred rent.
When cash payments in a period were greater than the expense recognized, prepaid rent would be capitalized on the balance sheet with a debit balance. This was considered a prepayment, which is an asset, due to more rent being paid rent receivable journal entry for than rent expense incurred. For an extensive explanation of prepaid rent and other rent accounting topics, see our blog, Prepaid Rent and Other Rent Accounting for ASC 842 Explained (Base, Accrued, Contingent, and Deferred).